Nowadays, sports bracelets and fitness trackers are among the most interesting gadgets. Bracelets of different colors and surface finish are «clever» accessories helping human trace his/her own activity.

Nowadays, sports bracelets and fitness trackers are among the most interesting gadgets. Bracelets of different colors and surface finish are «clever» accessories helping human trace his/her own activity.

The most informative and interesting sort of tourism is hiking. Hiking is a hobby that has no age or social limitations. Hiking was known to be healthful long ago. Even

This diet is the classic protein diet, but it differs from the meat one in that cheese proteins digest faster. The only shortcoming of the cheese diet is the high level of fats. Therefore, the amount of carbohydrates consumed should be minimized. However, the shortcoming mentioned is also the main merit of the cheese diet — fats decelerate digestion and strongly depress appetite.
 For a long time scientists have been dreaming of «correcting» genome, remove harmful mutations from it and prevent development of hereditary diseases. However, that became possible just a few years ago. There are three new technologies of genome editing. The earliest of them is the technology of zinc finger nucleases; the idea of this technology appeared as far back as 1980s.
For a long time scientists have been dreaming of «correcting» genome, remove harmful mutations from it and prevent development of hereditary diseases. However, that became possible just a few years ago. There are three new technologies of genome editing. The earliest of them is the technology of zinc finger nucleases; the idea of this technology appeared as far back as 1980s.
A while ago, research workers from the biotechnological company «Editas Medicine» announced at the scientific conference in Cambridge that they would be able to make pointwise changes in human genome by 2017.  Their creation was named «Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats» (CRISPR). The experts predict that technology developed will help people get rid of many congenital diseases, e.g. congenital Leber amaurosis. That will be real breakthrough in medicine. Moreover, the scientists promise that their creation will be simple and cheap, so it will be open to specialists from all over the world.
Their creation was named «Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats» (CRISPR). The experts predict that technology developed will help people get rid of many congenital diseases, e.g. congenital Leber amaurosis. That will be real breakthrough in medicine. Moreover, the scientists promise that their creation will be simple and cheap, so it will be open to specialists from all over the world.
Several technologies which allow to make directed changes in DNA nucleotide sequence of mammals were developed last years. At present, those new technologies are testing in mice:
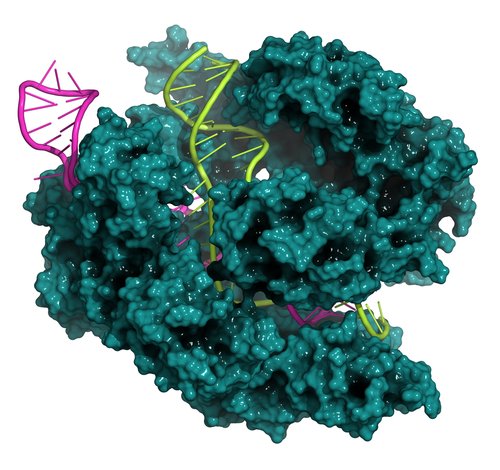 By the use of the method of TALEN nucleases, scientists make a break in the coding region of a gene and then they heal that break. In the experiments on mice, that technology was applied and mutation, that cause the development of one of the hereditary syndromes, was introduced into mouse genome. Then the authors of the experiment removed that mutation in the same way. Thus, they showed that TALEN allows changing genome efficiently.
By the use of the method of TALEN nucleases, scientists make a break in the coding region of a gene and then they heal that break. In the experiments on mice, that technology was applied and mutation, that cause the development of one of the hereditary syndromes, was introduced into mouse genome. Then the authors of the experiment removed that mutation in the same way. Thus, they showed that TALEN allows changing genome efficiently.
The method of zinc finger nucleases is not so effective as the methods mentioned above.
Methods of genome editing assure accurate delivery of therapeutic genes that allow retarding the processes of aging: telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), gene of the transcription factor FOXO3, and gene coding inhibitor of
Technologies described are not investigated and debugged enough. At the moment, careful modelling of those methods on mice is necessary. CRISPR and TALEN technologies are promising for the cure of serious illnesses of human.
 In 1959, it was established for the first time, that if we remove epiphysis in young rats, their life span shortens substantially compared to the control group. Data obtained were confirmed by other scientists. Later, it was shown that peptide extract of epiphysis named epytalaminum restore regular estrous cycles and sensitivity of hypothalamic sexual centers to oestrogens in mice — the mechanism that is believed to play a key role in
In 1959, it was established for the first time, that if we remove epiphysis in young rats, their life span shortens substantially compared to the control group. Data obtained were confirmed by other scientists. Later, it was shown that peptide extract of epiphysis named epytalaminum restore regular estrous cycles and sensitivity of hypothalamic sexual centers to oestrogens in mice — the mechanism that is believed to play a key role in
 Natural biological rhythms help an organism adapt to changeable environment. When those biorhythms are upset, the ability of an organism to resist unfavorable external forces decreases.
Natural biological rhythms help an organism adapt to changeable environment. When those biorhythms are upset, the ability of an organism to resist unfavorable external forces decreases.
pineal body is the main pace maker in human organism. That organ produces melatonin that depress free radical processes in an organism, thereby delaying aging.
 More and more information accumulates about the role of the pineal body as the main pace maker of functions of an organism. Light depresses production and secretion of melatonin, so the highest level of melatonin in the pineal body and blood is observed at night, while the lowest level — in the morning and in the daytime. When an organism ages, epiphysial function decline, so disorders of the rhythm of melatonin secretion appear and the level of melatonin secretion decreases.
More and more information accumulates about the role of the pineal body as the main pace maker of functions of an organism. Light depresses production and secretion of melatonin, so the highest level of melatonin in the pineal body and blood is observed at night, while the lowest level — in the morning and in the daytime. When an organism ages, epiphysial function decline, so disorders of the rhythm of melatonin secretion appear and the level of melatonin secretion decreases.
Mechanisms of geroprotector effect of melatonin and epytalaminum are not fully known. The ability of those substances to depress free radical processes in an organism could be important. Melatonin, as well as epitalaminum stimulate cells of the immune system and slow aging of the immune system down; they also normalize a number of
 Additions and Criticism:
Additions and Criticism:In experiments on mice, scientists found out that geroprotector effect of melatonin was not the same in all the cases and sometimes there was no effect at all. Moreover, it was established that melatonin given to experimental animals for a long period could increase the rate of neoplasms development.
 It is known for a long time that physical activity benefits health. That was Hippocrates who said that nothing exhausts an organism more than physical inactivity. That fact is confirmed by our everyday experience as well as scientific researches.
It is known for a long time that physical activity benefits health. That was Hippocrates who said that nothing exhausts an organism more than physical inactivity. That fact is confirmed by our everyday experience as well as scientific researches.
However, benefits of mental exercises, cognitive games and memory training were only hypothesized for a long time. However, in 2000s, neuroscientist from the University College of Irvine obtained convincing evidence that training improves brain health. Their investigations have shown that memory training, cognitive games and exercises have positive effect at neurons regeneration in human brain.
 Scientists from the European Society of Cardiology’s have proved that only 15 minutes of physical exercises a day decrease risk of death in elderly people at 51%. The report covering the results of that research was read at EuroPRevent conference in 2015.
Scientists from the European Society of Cardiology’s have proved that only 15 minutes of physical exercises a day decrease risk of death in elderly people at 51%. The report covering the results of that research was read at EuroPRevent conference in 2015.
In 2013, the Neurology journal published a paper submitted by scientists of the Rush University Medical Center, Chicago. That paper claims that regular mental activity maintains memory in elderly age.
There is abundant scientific evidence that regular physical and mental activity effect positively at physical and mental health. Physical exercises positively influence specific aspects of metabolism.
 World Health Organization (WHO) states that physical exercises is the best way for diseases prevention for elderly people as well as for young ones. According to WHO, physically active elderly people have lower indices of death from cardiologic, metabolic and some oncological diseases. They have biomarker profile which favour preventing the development of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes type 2, and help improving the health of bones. Physically active elderly people have also higher levels of functional health and cognitive function; they have lower risk of moderate and severe functional and role limitations.
World Health Organization (WHO) states that physical exercises is the best way for diseases prevention for elderly people as well as for young ones. According to WHO, physically active elderly people have lower indices of death from cardiologic, metabolic and some oncological diseases. They have biomarker profile which favour preventing the development of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes type 2, and help improving the health of bones. Physically active elderly people have also higher levels of functional health and cognitive function; they have lower risk of moderate and severe functional and role limitations.
Scientists believe that easy physical exercises for elderly people could be enough to decrise the risk of death substantially. Exercises could include active pacing, riding the bicycle, swimming and gymnastics. Furthermore, it was shown that people maintaining brain activity during the life by means of cognitive activity have lower level of β-amiloid protein that is believed to be one of the main reasons of Alzheimer’s desease.
 Modern scientists concluded that elderly people need not only physical, but also mental exercises. Unfortunately, this fact is not given appropriate consideration in our country. Developmental exercises and games are necessary not only for preschool child, but also for elderly people. It should be recommended to all our elderly people that they to do gymnastics for body and mind!
Modern scientists concluded that elderly people need not only physical, but also mental exercises. Unfortunately, this fact is not given appropriate consideration in our country. Developmental exercises and games are necessary not only for preschool child, but also for elderly people. It should be recommended to all our elderly people that they to do gymnastics for body and mind!
Norio Taniguchi, Eric Drexler, Robert Freitas
Science doesn’t stay in one place. Nanotechnologies and nanomaterials have found their application in medicine. At the eve of XXI century, such direction as nanomedicine has appeared. Nowadays this direction is rapidly developing, many nanotechnologies are already approved and patented for application in the field of drug delivery, diagnostics and treatment of some diseases, tissue regeneration and others.
Nanorobots and nanocomputers are the perfect examples of medical application of nanotechnologies.
Nanorobots — are the microscopic nanomachines of the future; they posses a high sensitivity, accuracy, and they can «obediently» execute the commands from the supervisory computer. With the help of nanorobots it is possible to provide the assembling of molecules, and in vivo tissue regeneration. Nanorobots are controlled by nanocomputers, which are characterized by highly accurate computation and programming.
Nowadays, nanodevices are used in the field of skin

It is very important for the treatment of
Currently, nanomatrices for regenerative medicine are widely used for in vitro tissue growing, but the technologies are improving and soon it will be possible to regenerate the organs and tissues directly in the human organism.
Injection of nanorobots will allow physicians to look inside the human organism, and it will extremely improve the accuracy of diseases diagnostics. These devices will demonstrate all human problems on «the large screen.»
Nanochips are extensively developing with the aim to fight with such intractable diseases as epilepsy. Nanochips will allow to control the convulsive seizures, analyzing the brain signals.
Furthermore, nanotechnologies offer exciting possibilities for their application in the field of personalized medicine, medical monitoring of patients, prostheses controlling.
All the mentioned application prospects are very promising, but there are some concerns and problems associated with the use of nanoparticles in medicine.

First of all, it is necessary to create a completely inert particles, which will not cause the immune response, when they will be ingested into the organism, and they will not interact with the organism’s molecules. Secondly, scientists still can not solve the problem of nanorobots toxicity for the organism: experiments on animals do not provide a decisive answer. And finally, there is a risk of damage of biomolecules, membranes, and cells from the invasion of nanodevices.
Despite these problems, we can say that nanomedicine — is a young and promising direction, and the elimination of negative consequences is about timing.
Andrjez Bartke, Luigi Ferrucci, Vincent Giampapa
Scientists are trying to determine the most definite aging biomarkers. Thus, in the 80s of the last century, Olovnikov AM has noted the telomere shortening as a potential aging biomarker. Last years it was discovered a number of molecular biomarkers.  For example, the scientists from King’s College London have first identified 22 molecular aging biomarkers in blood. And specialists from Stanford University School of Medicine have discovered some substances in blood of older mice. These substances caused the changes in brain of young animals, that are typical for the brain of old animals. The level of these substances increases with aging, and they appear to inhibit brain ability to produce the new neurones, which are important for memory formation and learning ability. The researchers from the University of Liverpool have created a new technique that will help other researchers to find genes, which are responsible for aging. They managed to identify genes in different tissues of humans and animals, which were exposed to multiple aging.
For example, the scientists from King’s College London have first identified 22 molecular aging biomarkers in blood. And specialists from Stanford University School of Medicine have discovered some substances in blood of older mice. These substances caused the changes in brain of young animals, that are typical for the brain of old animals. The level of these substances increases with aging, and they appear to inhibit brain ability to produce the new neurones, which are important for memory formation and learning ability. The researchers from the University of Liverpool have created a new technique that will help other researchers to find genes, which are responsible for aging. They managed to identify genes in different tissues of humans and animals, which were exposed to multiple aging.
 Example:
Example:
Scientists tend to make possible that fact when every person will be able to control aging process in their own organism. Currently about 100 possible aging biomarkers were proposed. In our country some clinical tests for some biomarkers are available: for example, the determination of biomarkers for some kinds of
 Aging biomarkers can be considered at four levels: physiological, cellular, molecular and chromosomal one. Physiological biomarkers include basic indicators of body functioning: eye and hearing examination, muscle mass, flexibility, aerobic endurance and others.
Aging biomarkers can be considered at four levels: physiological, cellular, molecular and chromosomal one. Physiological biomarkers include basic indicators of body functioning: eye and hearing examination, muscle mass, flexibility, aerobic endurance and others.
In order to determine the cellular aging biomarkers it should be taken a skin biopsy from the areas of skin, which seems to be in well condition. It is necessary to determine the quantity and quality of
 At the molecular level it is possible to determine more definite aging biomarkers. To determine the molecular aging biomarkers it should be taken the analysis of key hormones: human growth hormone, thyroid hormone, Q10, insulin sensitivity, heat shock proteins, oncogene analysis, serum levels of antioxidants.
At the molecular level it is possible to determine more definite aging biomarkers. To determine the molecular aging biomarkers it should be taken the analysis of key hormones: human growth hormone, thyroid hormone, Q10, insulin sensitivity, heat shock proteins, oncogene analysis, serum levels of antioxidants.
At the chromosomal level the aging biomarkers include determination of telomeres position and DNA degradation rate.
The scientists from the International Longevity Institute have developed the blood test, which will be able to monitor the DNA damage, and it will indicate the effect of
Let’s talk more detail about some prospective aging biomarkers.
Human Growth Hormone
A possible aging biomarker is a growth hormone. It is well known that with aging the level of growth hormone decreases.
 This decrease of growth hormone level is believed to be responsible for
This decrease of growth hormone level is believed to be responsible for
Thus, the members of Andrjez Bartke’s laboratory (Department of Physiology, Medical School, University of Southern Illinois) have obtained the data which show that the mice with impaired hypophysary function have longer lifespan, and overproduction of growth hormone lead to lifespan shortening.
 AGE accumulation
AGE accumulation
AGE (glycation end products) can damage cells in different ways: functional impairment of proteins through modifications,
AGE accumulation was demonstrated on various kinds of tissues from patients suffered from diabetes. Moreover, the researchers from the Dr. Monnier’s laboratory (Cleveland, USA) have demonstrated that AGE accumulation could be used as a marker of early death of mice.
Increase of
With aging the inflammatory cytokines are significantly activated. The examples are: 
Dr. Luigi Ferrucci (Department of Clinical Research Hospital in Harbour) has investigated a population of 473 elderly men and analyzed the interactions between level of testosterone and
He has found out the dependence between the testosterone level and
 Scientists have identified a number of aging biomarkers, but none of them are independent: only a set of markers can demonstrate a real aspect of aging. Separately none of biomarkers provide an exact forecast, mortality estimate or exactable lifespan, as well as a choice of the optimal therapeutic intervention to treat a particular disease. Therefore, researchers are trying to find more informative aging biomarkers to estimate the risk of disease development and to predict the disease outcome.
Scientists have identified a number of aging biomarkers, but none of them are independent: only a set of markers can demonstrate a real aspect of aging. Separately none of biomarkers provide an exact forecast, mortality estimate or exactable lifespan, as well as a choice of the optimal therapeutic intervention to treat a particular disease. Therefore, researchers are trying to find more informative aging biomarkers to estimate the risk of disease development and to predict the disease outcome.
Matthias Stadtfeld, Hongyan Zhou
 Obtaining of mammalian pluripotent stem cells from fibroblasts of adult animals became a real breakthrough in Cell Biology. Due to addition of transcription factors to fibroblasts, the cells of adult animals are able to transform into any cell of the organism. Such cells were called induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs). In 2008 this experiment was first repeated in human cells.
Obtaining of mammalian pluripotent stem cells from fibroblasts of adult animals became a real breakthrough in Cell Biology. Due to addition of transcription factors to fibroblasts, the cells of adult animals are able to transform into any cell of the organism. Such cells were called induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs). In 2008 this experiment was first repeated in human cells.

On September 12, 2014 in Japan the
Pluripotent Stem Cells are able to transform into any type of adult organism cells. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells — are the cells, driven from somatic cells of adult organism.
 The obtaining technology of these cells is quite simple: in vitro the somatic cells are driven from a patient skin biopsy; then the cells are converted into iPSCs, and these «fresh» pluripotent cells are differentiated into the necessary cell type and, finally, they are transferred to the patient.
The obtaining technology of these cells is quite simple: in vitro the somatic cells are driven from a patient skin biopsy; then the cells are converted into iPSCs, and these «fresh» pluripotent cells are differentiated into the necessary cell type and, finally, they are transferred to the patient.
IPSCs are expected to give the opportunity to replace the sick or lost cells directly into the tissues, regenerating the body literally by cells. It will be suitable for the treatment of many diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, diabetes, and consequences of heart attack.
Furthermore, on the immortal iPSCs cultures it can be studied many rare genetic diseases, as well as developed and tested the methods to fight such diseases. iPSCs have already been obtained for the treatment of such diseases, as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (Lou Gehrig’s disease), Rett syndrome, Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), insufficiency of Antitrypsin α1, Familial Hypercholesterolemia, as well as for treatment of various cardiac diseases.
 The downside of iPSCs application is a possibility of malignant transformation of this cells in the human organism. In addition, talking about brain diseases, there are a number of additional problems of iPSCs transplantation because of outstanding complexity of the human nervous system.
The downside of iPSCs application is a possibility of malignant transformation of this cells in the human organism. In addition, talking about brain diseases, there are a number of additional problems of iPSCs transplantation because of outstanding complexity of the human nervous system.
Despite potential concerns, nowadays, the iPS cells technology is one of the most promising methods for studying the molecular mechanisms of cellular abnormalities, as a part of personalized medicine; creation of the effective test systems for searching and screening of pharmaceutical preparations; and for the development of cell therapy approaches to treat various human diseases.